Within this digital landscape, the GPU, or graphics processing unit, plays a vital role in rendering premium images and speeding up intricate calculations. Regardless of whether you are a gamer, a content creator, or an artificial intelligence researcher, grasping GPU specifications is crucial for making educated decisions about which GPU meets your needs. As technology progresses, the detailed design and specifications of GPUs have become critical factors that define their overall efficiency.
When evaluating GPU specs, several factors come into focus, such as clock speed, memory size, memory bandwidth, and the number of cores. Each of these specifications can greatly affect how well a GPU operates in various applications, from gaming to ML. By delving into these critical aspects, you can more effectively recognize how they affect a GPU's ability to process demanding applications and detailed graphics effectively.
Core Clock Speed
Main clock speed is an important a crucial factors that influences the efficiency of a graphics card. It is the frequency at which the GPU's cores operate, generally expressed in MHz or gigahertz. A greater frequency often indicates that the GPU can perform more instructions per unit of time, resulting in enhanced capabilities in many programs, notably in gaming and heavy tasks.
Yet, clock speed alone does not only determine total GPU capability. Factors such as the count of cores, the architecture of the GPU, and heat control also play significant influence. A GPU with a decreased frequency but more cores may excel a higher frequency GPU with less cores in specific tasks. Consequently, understanding frequency in the context of different features is vital for a comprehensive assessment of GPU potential.
When evaluating GPUs for particular use scenarios, such as gaming or media production, it is important to consider both the base clock speed and the accelerated clock speed. The base clock speed indicates the minimum frequency the GPU functions at under normal conditions, while the boost clock can achieve greater frequencies temporarily when heat and energy constraints allow. This dynamic behavior can significantly influence performance in practical scenarios.
Memory Type and Size
The memory type and size of a graphics processing unit are critical factors that influence its efficiency and effectiveness. Contemporary GPUs typically use GDDR (Graphics Double Data Rate) memory, with versions such as GDDR5, GDDR6, and the newer GDDR6X. These categories of RAM are designed for greater bandwidth, enabling faster data transfer between the GPU and its RAM. The developments in memory technology have allowed GPUs to manage more sophisticated graphics and larger datasets, rendering them crucial for video games, video production, and AI tasks.
In addition of the type of RAM, the size of the memory plays a important role in determining a GPU's capability. A GPU with a bigger size of memory, often quantified in gigabytes, can accommodate more assets, models, and data, which is particularly advantageous for high-resolution gaming and three-dimensional software. Common memory sizes range from 4GB to 24GB and more, with higher capacities becoming ever important for intensive use cases. When selecting a GPU, understanding the size of the memory helps ensure that it can accommodate the requirements of current software and tasks.
Finally, the bandwidth, which is related to both the memory type and capacity, influences how quickly a GPU can access and analyze data. Increased bandwidth enables smoother performance during intensive tasks, such as graphic rendering or executing advanced simulations. When evaluating GPUs, it is important to take into account not only the quantity of RAM but also the type of memory and speed in order to get a comprehensive understanding of their capabilities in real-world applications.
CUDA Cores and Processing Power
CUDA cores are the fundamental building blocks of NVIDIA graphics processing units, serving as the parallel processing units that handle multiple calculations at once. The number of CUDA processing units can greatly impact a GPU's overall performance, especially in tasks that require high computing power, such as video games and scientific simulations. Typically, gpuprices of CUDA cores indicates improved performance possibilities, but the architecture and operating frequency of the GPU also play a critical role in defining the real processing power.
In addition to the total count of CUDA processing units, the design of the GPU is essential for optimizing performance. NVIDIA's different architectures, such as Pascal, Turing, and NVIDIA Ampere, introduce various improvements in processing efficiency and power management. These enhancements can affect how effectively CUDA cores work in tandem, leading to better performance metrics in real-world applications. Improved frame rates in video games and faster rendering times in graphics software often result from progress in both core count and architectural design.
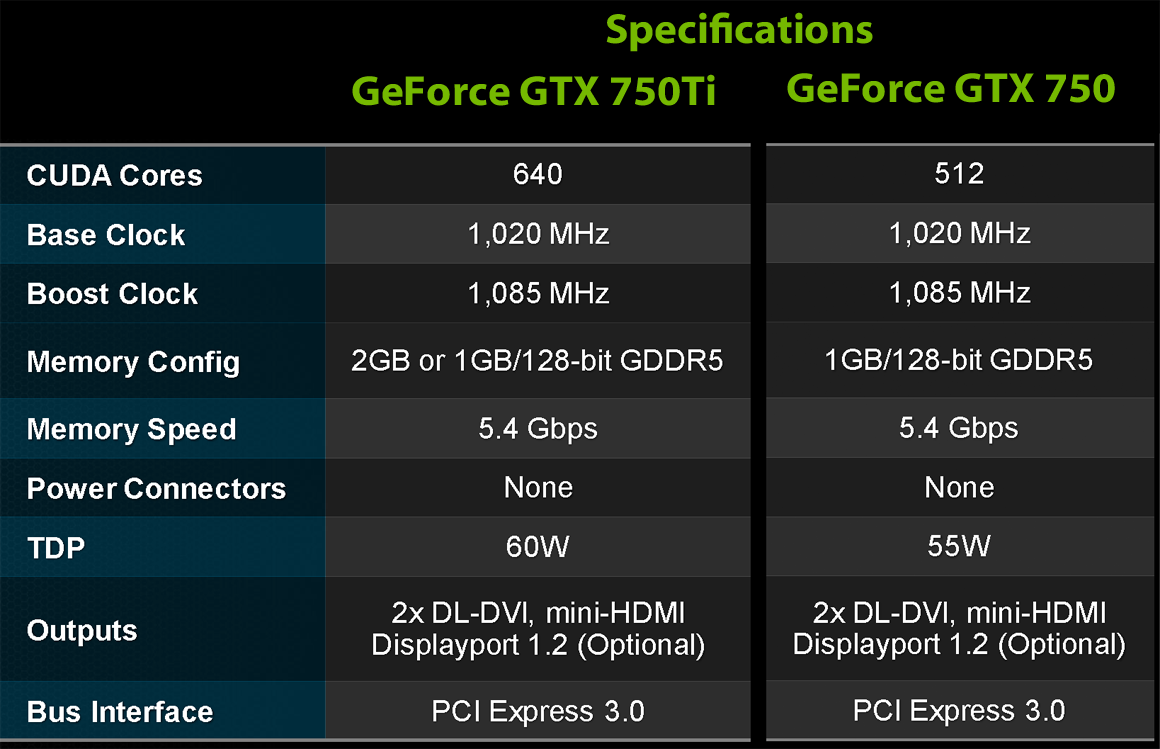
Grasping the processing power of a GPU goes beyond just the number of CUDA processing units. Factors such as the operating frequency, data transfer capacity, and thermal design power all play a part in a GPU's effectiveness in performing intensive tasks. A GPU equipped with a strong quantity of CUDA processing units that reaches elevated frequencies can outperform one with more cores but a reduced operating frequency. Thus, when evaluating GPU specifications, looking at the complete view of each of these factors is crucial for making informed decisions regarding effectiveness.
